Press reviews
#Immunotherapy #FoodAllergy #Peanut
#Desensitization
Peanut allergy is one of the most severe and persistent food allergies. It affects up to 3% of the pediatric population in Western countries. It is a major cause of anaphylaxis and has a significant impact on the quality of life of patients and their families. The constant fear of accidental exposu...
Peanut allergy is one of the most severe and persistent food allergies. It affects up to 3% of the pediatric population in Western countries. It is a major cause of anaphylaxis and has a significant impact on the quality of life of patients and their families. The constant fear of accidental exposu...
Read more

#Lupus #SLE #Baricitinib #JAK #Autoimmunity
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by the aberrant production of autoantibodies and multisystem inflammation. Its clinical expression is heterogeneous and unpredictable, with acute flares alternating with remission phases, making management particularly complex. SLE pred...
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by the aberrant production of autoantibodies and multisystem inflammation. Its clinical expression is heterogeneous and unpredictable, with acute flares alternating with remission phases, making management particularly complex. SLE pred...
Read more

#Sepsis #Homocysteine #Biomarker #Mortality
#PersonalizedMedicine #IntensiveCare
Sepsis is an exacerbated systemic inflammatory response triggered by infection, leading to acute organ dysfunction. It remains one of the leading causes of death in hospital settings. Despite advancements in early diagnosis, resuscitation protocols, and antimicrobial treatments,...
Sepsis is an exacerbated systemic inflammatory response triggered by infection, leading to acute organ dysfunction. It remains one of the leading causes of death in hospital settings. Despite advancements in early diagnosis, resuscitation protocols, and antimicrobial treatments,...
Read more
#Pedagogy #EscapeGame #EscapeRoom #NursingCare
#Training
The teaching of nursing science faces a persistent paradox. While professional training expectations are increasingly evolving toward complex and cross-disciplinary competencies, traditional pedagogical methods struggle to meet these demands. Lectures and standardized assessments demonstrate significant limitati...
The teaching of nursing science faces a persistent paradox. While professional training expectations are increasingly evolving toward complex and cross-disciplinary competencies, traditional pedagogical methods struggle to meet these demands. Lectures and standardized assessments demonstrate significant limitati...
Read more

#Pregnancy #COVID-19 #Vaccination
#VaccineSafety #SARS
Pregnant women are at increased risk of severe complications when infected with SARS-CoV-2. Infection can lead to adverse outcomes such as preterm birth, the need for intensive care hospitalization, and in the most severe cases, maternal or neonatal death. This vulnerability is due to immunological and p...
Pregnant women are at increased risk of severe complications when infected with SARS-CoV-2. Infection can lead to adverse outcomes such as preterm birth, the need for intensive care hospitalization, and in the most severe cases, maternal or neonatal death. This vulnerability is due to immunological and p...
Read more

2025-04-29
Pregnancy under surveillance: infections—who really protects?
Public Health and Social Medicine
#Infection #Pregnancy #Immunization #Immunity
#Vaccination
Pregnancy is a critical period when it comes to infectious risks, especially in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). Maternal infections are responsible for high rates of maternal and neonatal morbidity, including miscarriages, prematurity, low birth weight, and even infant death. Despite global prioritiz...
Pregnancy is a critical period when it comes to infectious risks, especially in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). Maternal infections are responsible for high rates of maternal and neonatal morbidity, including miscarriages, prematurity, low birth weight, and even infant death. Despite global prioritiz...
Read more
#Malaria #Vaccination #GA2 #AttenuatedParasites
Despite decades of efforts, preventive campaigns, mass distribution of bed nets, and antimalarial treatments, malaria continues to claim more than 600,000 lives each year. Children under five years old represent the majority of these deaths, particularly in high-transmission areas of sub-Saharan Africa. This situation under...
Despite decades of efforts, preventive campaigns, mass distribution of bed nets, and antimalarial treatments, malaria continues to claim more than 600,000 lives each year. Children under five years old represent the majority of these deaths, particularly in high-transmission areas of sub-Saharan Africa. This situation under...
Read more

#PostpartumMalaria #MalariaPrevention #MaternalRisk #Artemisinin
#InnovativeStrategy #PublicHealth #EndemicAreas
In regions with high malaria prevalence, pregnant women are a high-risk group. Multiple targeted measures, such as intermittent preventive treatment during pregnancy and prompt management of symptomatic episodes, can be implemented. However, after...
In regions with high malaria prevalence, pregnant women are a high-risk group. Multiple targeted measures, such as intermittent preventive treatment during pregnancy and prompt management of symptomatic episodes, can be implemented. However, after...
Read more

#MalariaVaccine #R21MatrixM #Malaria #Vaccination #SMC #InsecticideTreatedNets
#Immunization #VaccineAcceptability
Despite decades of efforts, malaria remains a major health threat to populations in sub-Saharan Africa. In 2022, the World Health Organization estimated 233 million cases on the continent, resulting in 580,000 deaths. Far from receding, the disease is show...
Despite decades of efforts, malaria remains a major health threat to populations in sub-Saharan Africa. In 2022, the World Health Organization estimated 233 million cases on the continent, resulting in 580,000 deaths. Far from receding, the disease is show...
Read more

#PfSPZ #Vaccination #Malaria #Immunogenicity
In 2023, malaria affected more than 263 million people worldwide and caused nearly 600,000 deaths, according to the WHO. These alarming numbers have remained almost unchanged over the past decade, illustrating the stagnation of global efforts to eliminate this parasitic disease, despite massive investments. While the developme...
In 2023, malaria affected more than 263 million people worldwide and caused nearly 600,000 deaths, according to the WHO. These alarming numbers have remained almost unchanged over the past decade, illustrating the stagnation of global efforts to eliminate this parasitic disease, despite massive investments. While the developme...
Read more

#AllergicRhinoconjunctivitis #IgG4 #Allergoid #BirchPollen #Immunotherapy
Allergic rhinoconjunctivitis (ARC) induced by birch pollen is one of the most common forms of seasonal allergic disease in Europe. It affects up to 40% of the population, with a high concentration of cases in temperate regions where birch trees are prevalent. This condition presents with a combin...
Allergic rhinoconjunctivitis (ARC) induced by birch pollen is one of the most common forms of seasonal allergic disease in Europe. It affects up to 40% of the population, with a high concentration of cases in temperate regions where birch trees are prevalent. This condition presents with a combin...
Read more

#SeasonalAllergicRhinitis #Probiotics
#Prebiotics #GutMicrobiota
Seasonal allergic rhinitis (SAR) is a chronic inflammatory condition of the upper airways, driven by an inappropriate immune response to environmental allergens such as pollen. It is characterized by classic symptoms — sneezing, runny nose, nasal congestion, and itching — that significantly impair qualit...
Seasonal allergic rhinitis (SAR) is a chronic inflammatory condition of the upper airways, driven by an inappropriate immune response to environmental allergens such as pollen. It is characterized by classic symptoms — sneezing, runny nose, nasal congestion, and itching — that significantly impair qualit...
Read more

#ParkinsonsDisease #Osteoporosis #FractureRisk
#FRAX #Prevention
In patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD), the risk of fracture is significantly higher than in the general population, particularly among the elderly. This heightened vulnerability stems from a combination of motor and metabolic factors. Frequent falls—linked to bradykinesia and postural instability—occ...
In patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD), the risk of fracture is significantly higher than in the general population, particularly among the elderly. This heightened vulnerability stems from a combination of motor and metabolic factors. Frequent falls—linked to bradykinesia and postural instability—occ...
Read more

#Parkinsons #VR #Rehabilitation #Balance
#Exergaming
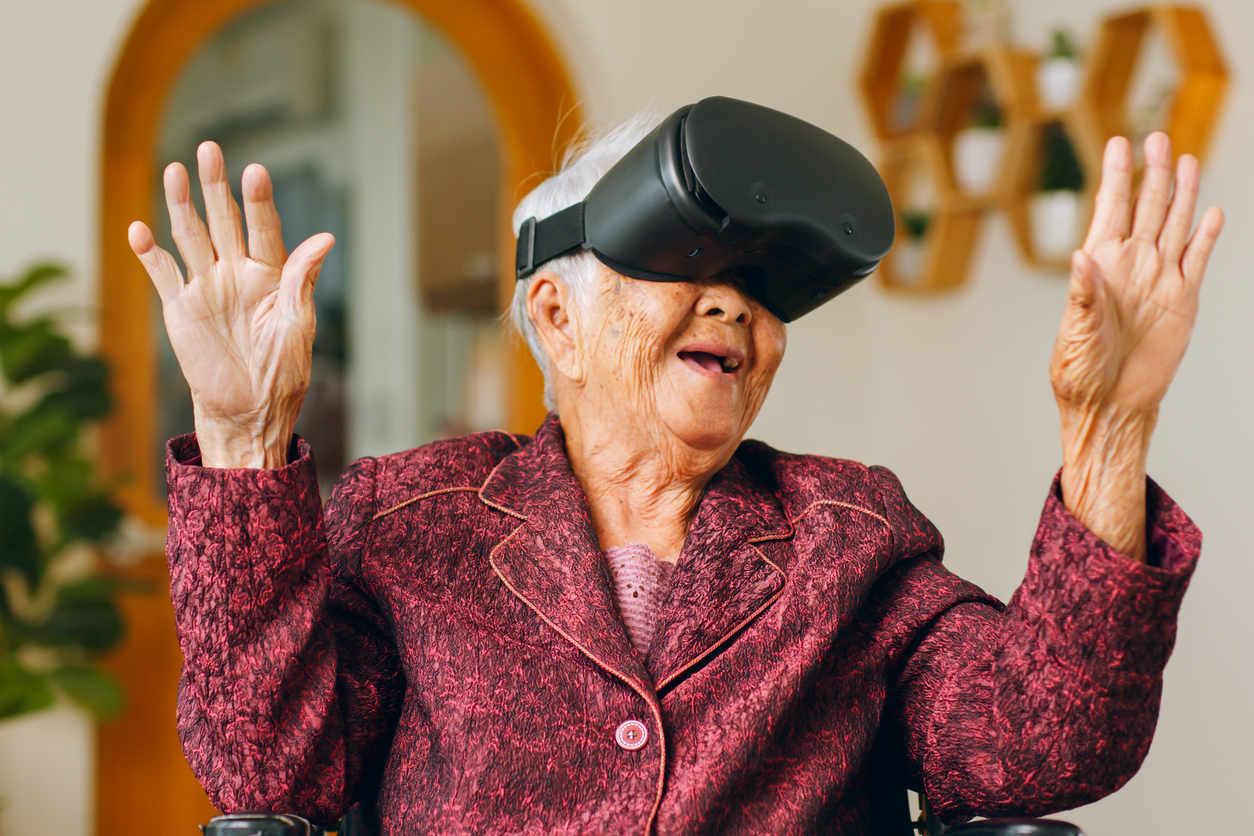
In patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD), balance disorders are among the most disabling symptoms. Linked to impaired postural control, coordination, and fine motor skills, they significantly increase the risk of falls, leading to injury, loss of independence, and a marked decline in quality of life. Thes...
In patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD), balance disorders are among the most disabling symptoms. Linked to impaired postural control, coordination, and fine motor skills, they significantly increase the risk of falls, leading to injury, loss of independence, and a marked decline in quality of life. Thes...
Read more

#Parkinson #Cognition #Inflammation #IL6 #Entacapone #MoCA
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder primarily characterized by motor symptoms such as tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia. However, in moderate to advanced stages, non-motor symptoms—particularly cognitive impairments—become increasingly common, affecting memory, attention, exec...
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder primarily characterized by motor symptoms such as tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia. However, in moderate to advanced stages, non-motor symptoms—particularly cognitive impairments—become increasingly common, affecting memory, attention, exec...
Read more
